Fluid Retention: A Senior’s Guide to Understanding
Fluid Retention: A Senior’s Guide to Understanding, Preventing, and Thriving
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, and one common challenge that many seniors face is fluid retention. This condition, also known as edema, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body’s tissues. While it can be uncomfortable and even alarming, understanding the reasons behind fluid retention and taking proactive steps can significantly improve your quality of life as a senior.
Understanding Fluid Retention: Types and Causes
There are several types of fluid retention, each with its own set of causes:
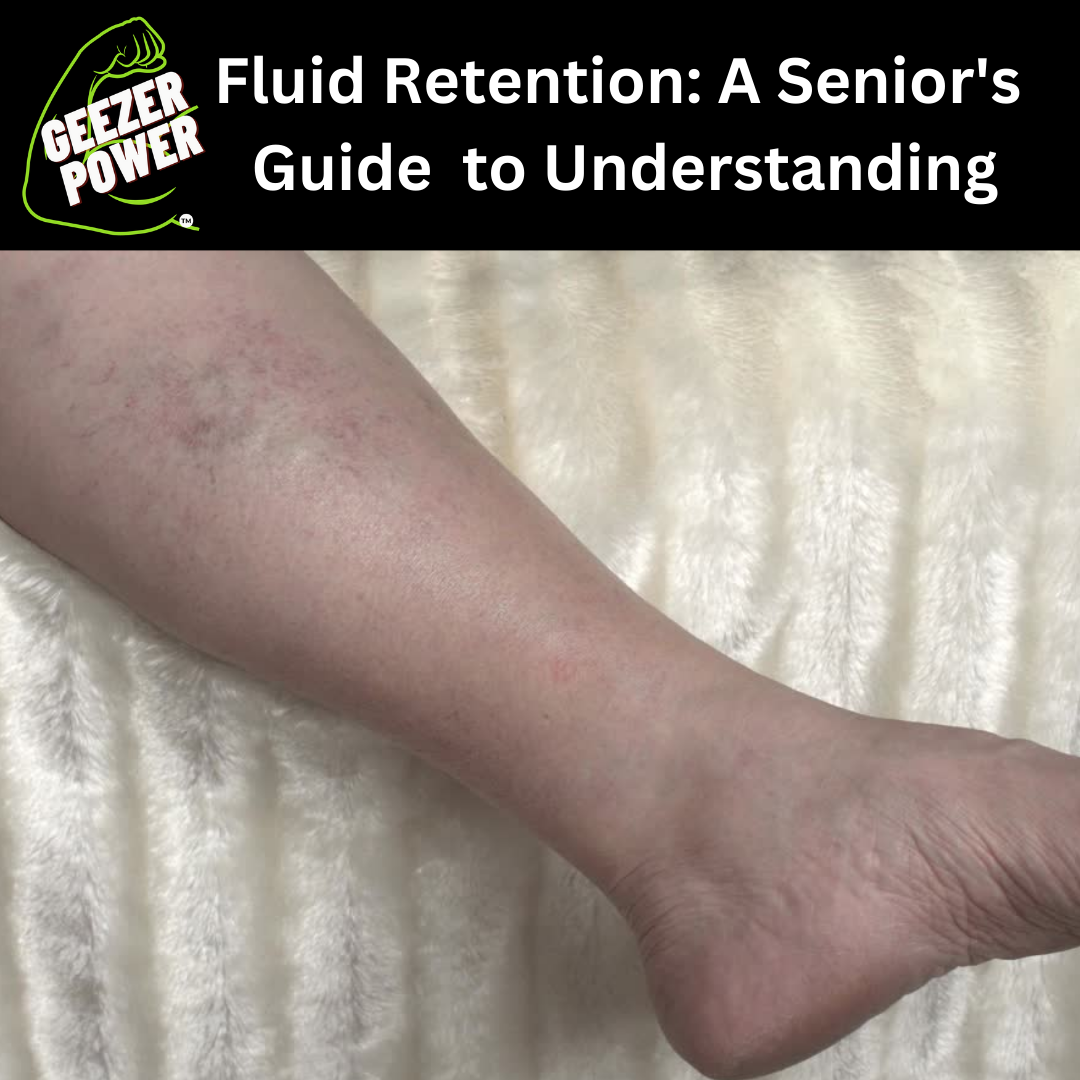
Peripheral Edema: This type of fluid retention typically affects the legs, ankles, and feet. It can be caused by factors such as standing or sitting for long periods, certain medications, venous insufficiency, or heart failure.
Pulmonary Edema: Fluid buildup in the lungs can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. Heart failure, pneumonia, and certain lung conditions can contribute to pulmonary edema.
Cerebral Edema: This occurs when fluid accumulates in the brain, often due to conditions like head trauma, stroke, or brain tumors.
Ascites: Abdominal fluid retention, known as ascites, can result from liver disease, cancer, or certain infections.
How Fluid Retention Starts and Escalates
Fluid retention can start gradually, often as a result of lifestyle factors, medical conditions, or medications. As we age, our bodies may become less efficient at regulating fluid balance, leading to an increased risk of edema. Factors such as poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, hormonal changes, and certain medications can all contribute to fluid retention in seniors.
Preventing and Managing Fluid Retention
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to prevent and manage fluid retention:
Stay Active: Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve circulation and lymphatic drainage, reducing the risk of fluid buildup in the legs and feet.
Follow a Healthy Diet: Limiting salt intake and consuming potassium-rich foods can help regulate fluid balance in the body.
Stay Hydrated: While it may seem counterintuitive, staying hydrated can actually help prevent fluid retention by encouraging proper fluid balance in the body.
Elevate Your Legs: If you experience swelling in your legs or feet, elevating them above heart level can help reduce fluid buildup.
Manage Underlying Conditions: Properly managing conditions such as heart disease, kidney disease, and diabetes can help prevent complications associated with fluid retention.
Benefits of Preventive Actions
Taking proactive measures to prevent fluid retention offers numerous benefits for seniors:
Improved Mobility: By reducing swelling and discomfort, preventive actions can help seniors maintain their mobility and independence.
Better Heart Health: Many preventive measures, such as exercise and a healthy diet, also benefit heart health, reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Enhanced Quality of Life: By addressing fluid retention early on, seniors can enjoy a higher quality of life, free from the discomfort and limitations associated with edema.
Thriving with a Proactive Approach
By adopting a proactive approach to fluid retention, seniors can achieve a higher quality of life and minimize the risk of complications. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and staying hydrated are all key components of a healthy lifestyle that can help prevent fluid buildup and promote overall well-being.
Possible Complications of Fluid Retention
Ignoring fluid retention can lead to several complications, including:
Skin Infections: Prolonged swelling can lead to skin breakdown and increase the risk of infections such as cellulitis.
Reduced Mobility: Severe swelling can impair mobility and increase the risk of falls and injuries.
Worsening of Underlying Conditions: Fluid retention can exacerbate underlying health conditions such as heart failure, kidney disease, and diabetes, leading to further complications.
In conclusion, fluid retention is a common challenge for seniors, but with knowledge, proactive measures, and proper management, it can be effectively addressed. By understanding the types and causes of fluid retention, implementing preventive actions, and seeking timely medical attention when needed, seniors can enjoy a higher quality of life and continue to thrive as they age.

